Can’t find your discipline or profession? Write to us and we’ll
do our best to work something out.
Every project is unique.
We adjust our services to your needs.
Libera Reference Master Oscillator (RMO) is used as a low-noise and stable source of an RF signal which can serve for synchronization of different devices (e.g. LLRF stations in an accelerator).
Libera Reference Master Oscillator (RMO) general description:
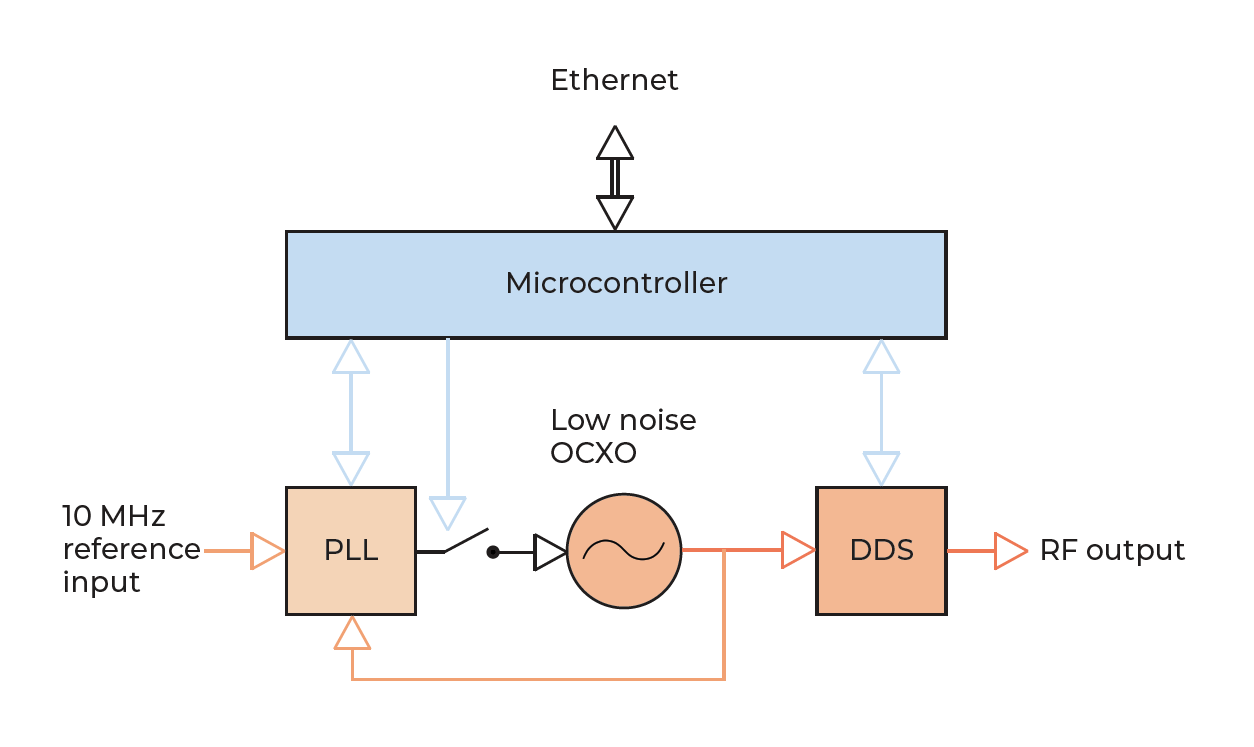
Libera RMO is used as a low-noise and stable source of an RF signal which can serve for synchronization of different devices (e.g. LLRF stations in an accelerator). The core of the device is a low-noise oven controlled crystal oscillator (OCXO) which guarantees long-term stability. Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS) technology is used to generate output RF signals at different frequencies. The DDS is utilized to provide frequency sweep functionality.
Optionally the Libera RMO can be locked to an external reference RF signal (e.g. a rubidium oscillator or GPS signal) by means of phase locked loop (PLL). In this way even better long-term stability can be achieved.
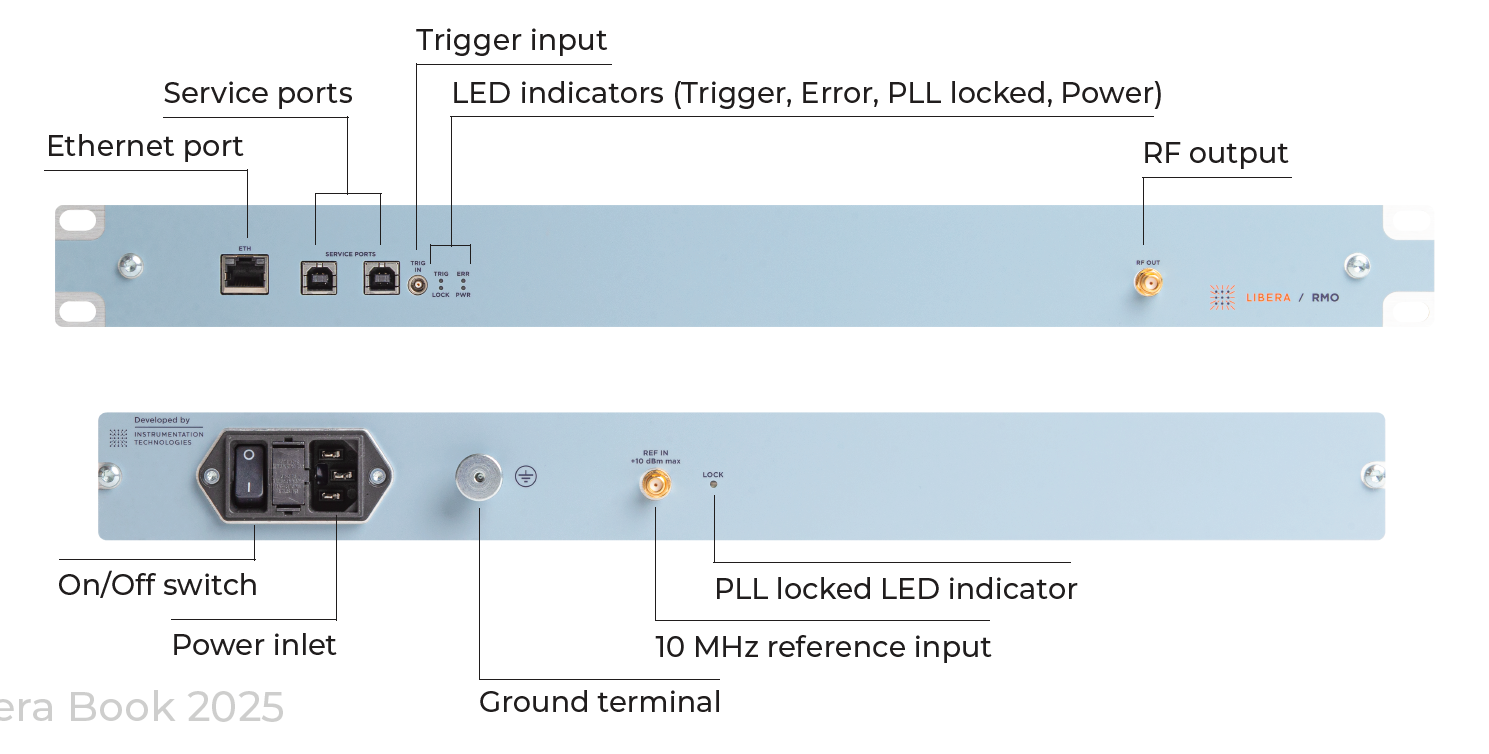
Libera RMO front and back panel:
Benefits:
Compatible with other Libera products:
| General product code | LRMO |
| Supported frequency ranges | 50 Hz - 3120 MHz |
| RF output | 1, SMA connector, 50 Ω |
| Nominal RF output power | +15 dBm at least |
| RF output power stability | 0,05 dB/K |
| Phase noise (integrated from 10 Hz to 10 MHz) | Max: < 90 fs RMS Typically: 40 - 60 fs RMS |
| Harmonic suppression | < 50 dBc up to 5th harmonic |
| Frequency stability in free running mode (Allan Deviation) | 5*10^-11 (Allan deviation) |
| RF output return loss | -15 dB |
| RF reference input | 1, SMA connector, 50 Ω |
| RF reference input frequency | 10 MHz ± 20 Hz |
| RF reference input power | -20 dBm - +10 dBm |
| PPL lock time | < 30 s |
| Stability operation temperature range | 20 - 25 °C |
| Operating relative humidity range | 0 - 80 % |
| Dimensions | H: 1 U, W: 19" (rack mountable), D: 358 mm |
| Locking to an external 10 MHz reference signal by means of a PLL |
| Frequency sweep |
| Frequency setting on trigger |
| Remote control via Ethernet |
| EPICS IOC |
*Customizations are possible.
Libera Reference Master Oscillator is used at the following labs:
Can’t find your discipline or profession? Write to us and we’ll
do our best to work something out.
We adjust our services to your needs.